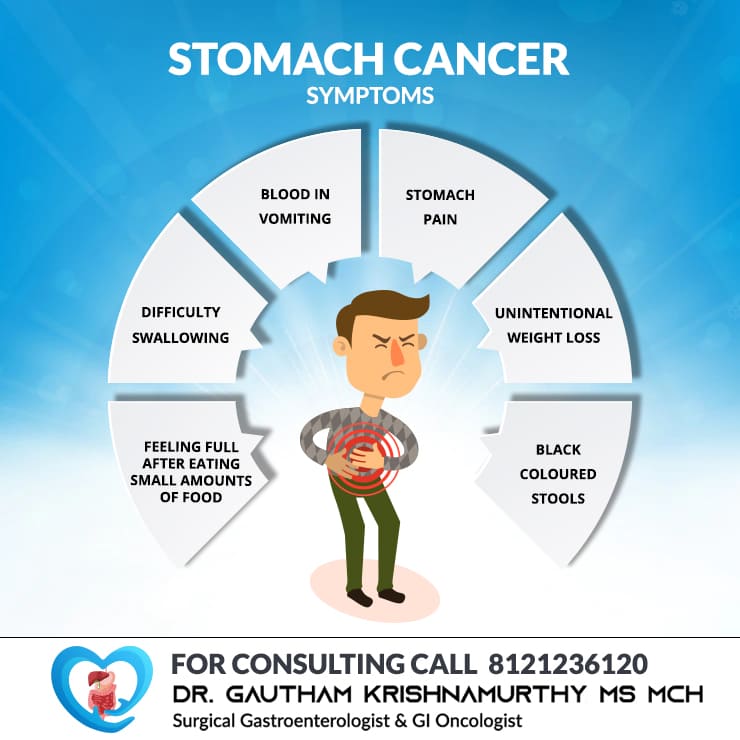
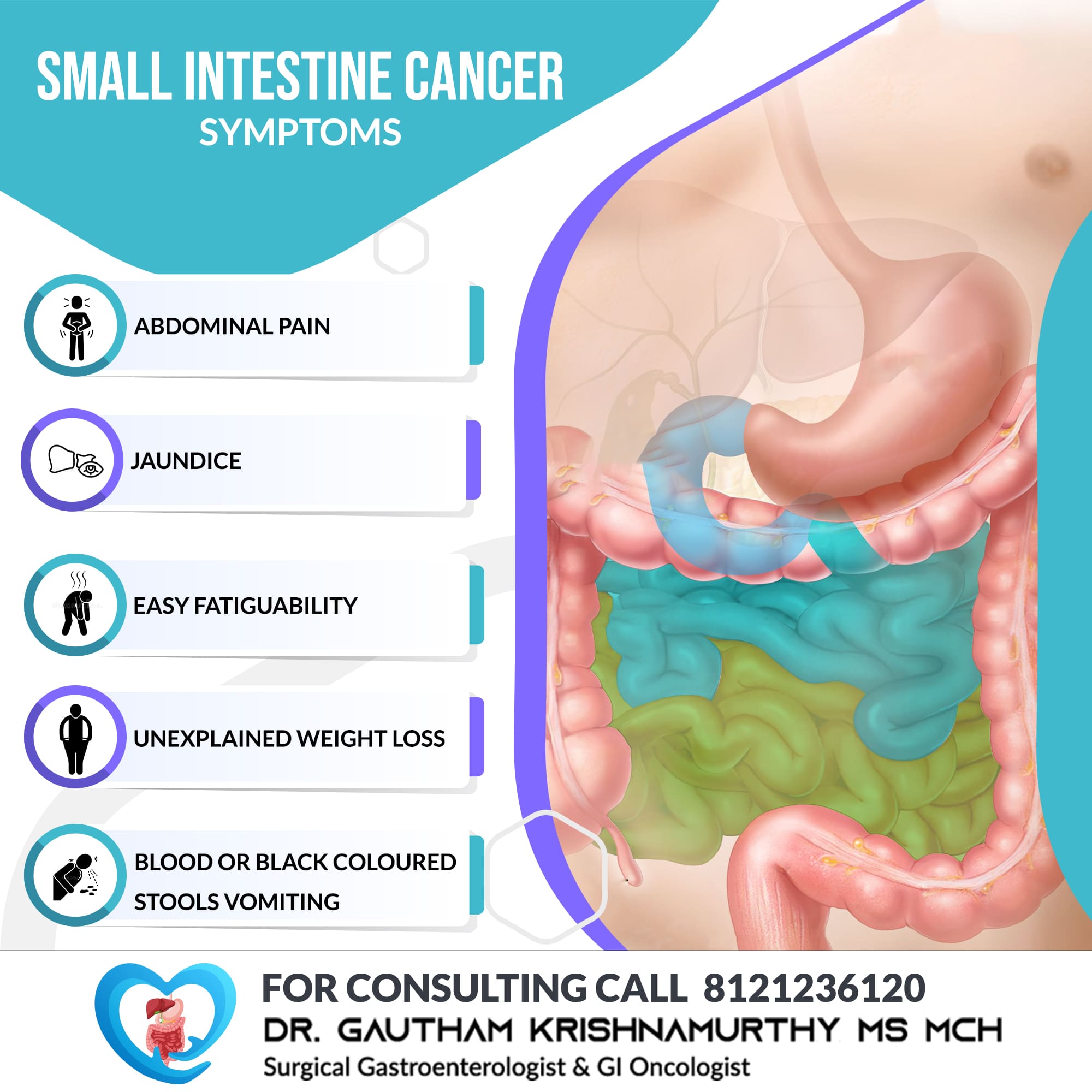
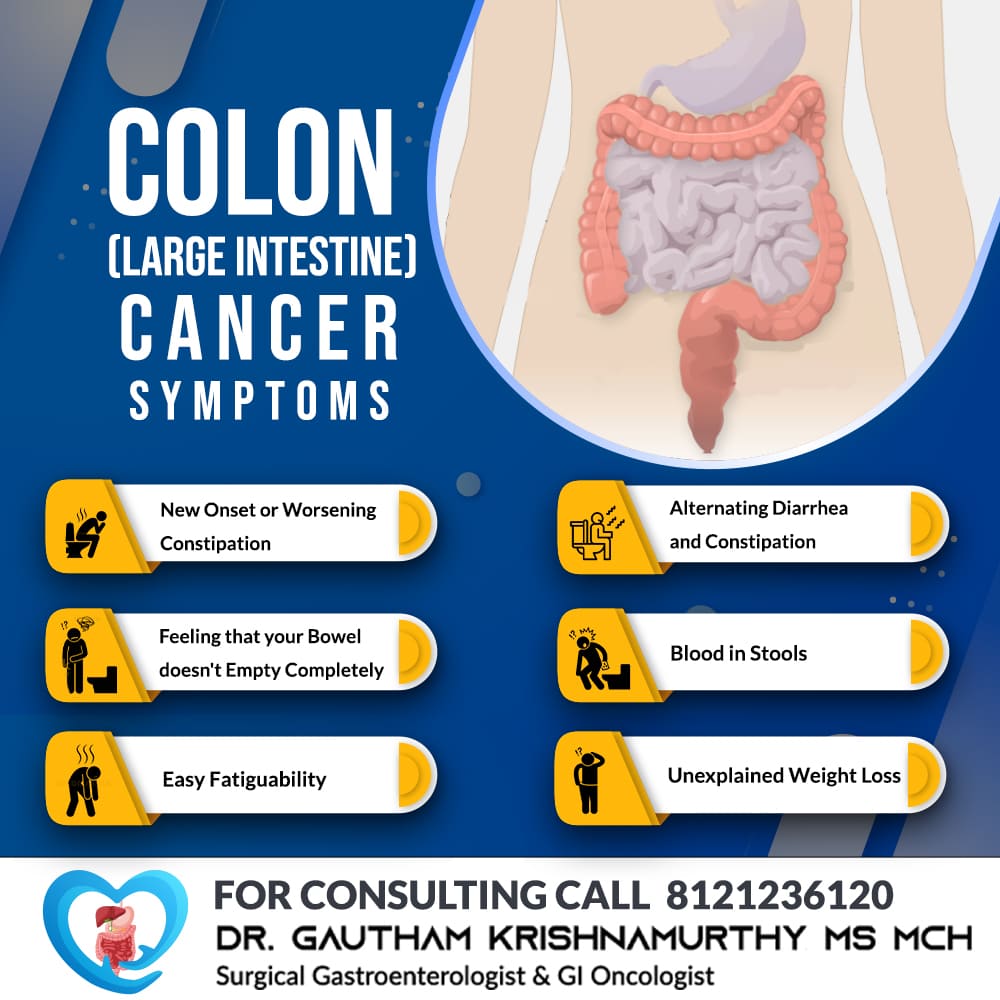
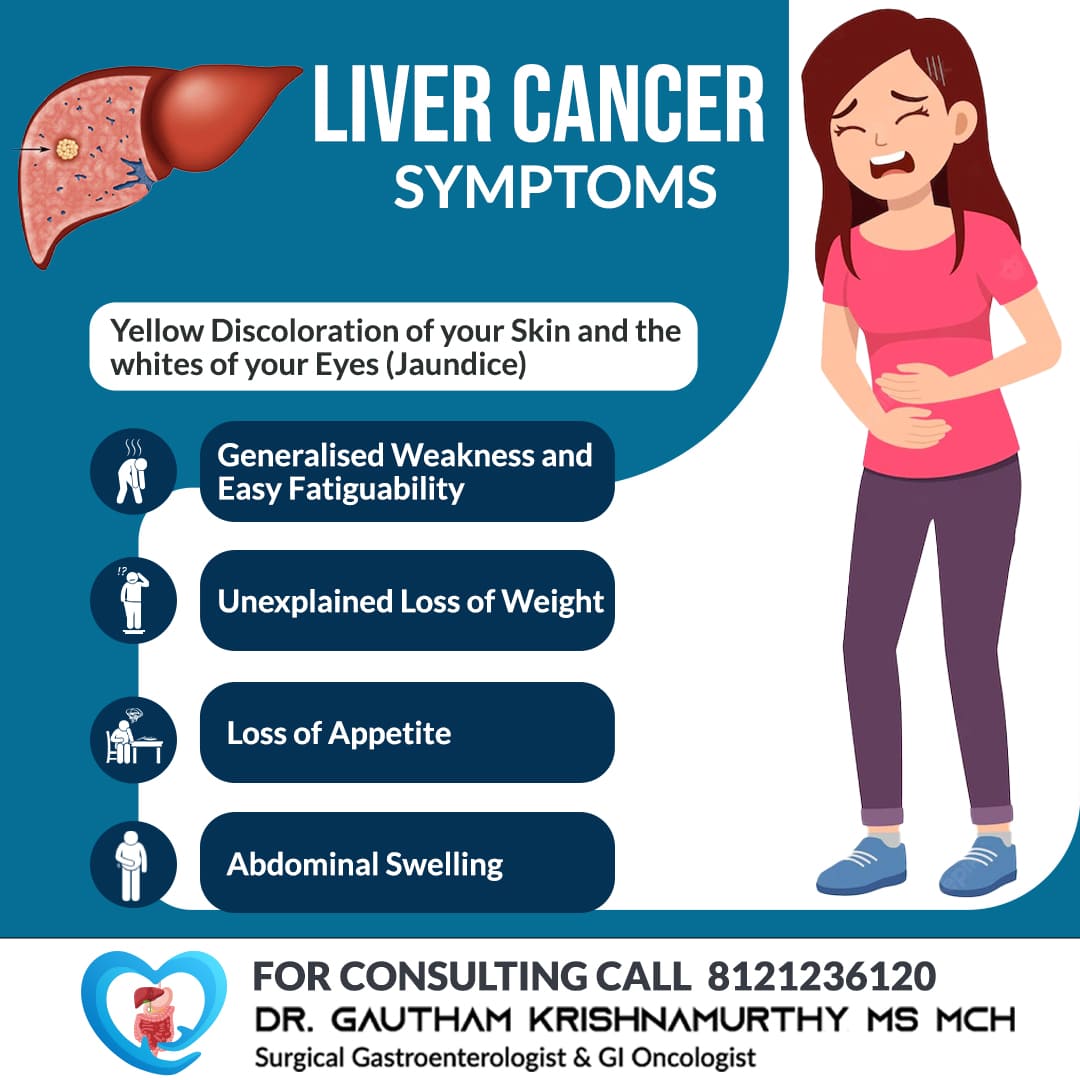
Cancer
Cancer refers to the abnormal growth of abnormal cells. Effective treatment is available for all cancers. Cancers are potentially curable at early stages.
World health awareness days
World Health Organizations (WHO) and The United Nations urge everyone including individuals, organization and communities worldwide to take active part and educate others with real scientific data related to health issues. Every individual should take part in this observance to help in promoting healthier lifestyle.